If one picture can be worth a thousand words (depending, of course, on the relative quality of both picture and words), the same is surely no less true of a map. I regret that it was so late in my career when I truly began to understand the illustrative power of a good map. Take the following example, drawn from Dave Leip's Atlas of Presidential Elections, which is the very best political map site out there in my doubtless insufficiently humble opinion. (Be advised, though, that old Dave does the switcheroo on the traditional pattern in these parts by using red for the Democrats and blue for the Repubs, apparently following the approach common in Europe and elsewhere.)
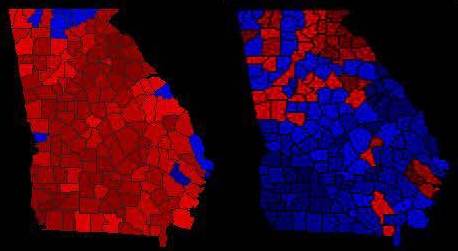
What we have here is a juxtaposition of county-level voting patterns from the 1960 and 1964 presidential elections in Georgia. That's in literal terms, however, for what it really amounts to is a snapshot of the GOP's coming-out party in Georgia, an event simultaneously celebrated and bemoaned in four other southern states in 1964. Striking as it seems, even in retrospect, this day had been coming since the late 1930s when white southerners began to cast a wary eye toward the national Democratic party's increasingly cozy relationship with organized labor and northern blacks, whose ranks had been swelled by a flood tide of southern in-migrants seeking greater freedom and opportunity, but also fleeing a place where they could not vote for one where they could. Sparked by a new civil rights plank in the Democratic platform, the 1948 Dixiecrat insurgency bled over into significant crossovers into the Eisenhower camp in 1952, when the GOP claimed four of the old Confederate states and 1956, when it picked up five. The Republicans' economic conservatism had also begun to resonate with white-collar whites in the urban and emerging suburban South by the end of the 1950s.
In the 1960 vote, which very much suggested Republicanism was on the march in Georgia, albeit not exactly at double-time, Republican Richard M. Nixon actually bested his former boss Dwight D Eisenhower, who had captured close to one third of the popular vote in Georgia in both 1952 and 1956. Nixon's 37% percent showing primarily reflected the growth of Republican support in Georgia's urban counties, especially Fulton. Although he ran a bit better than Ike in some rural counties as well, his numbers hovered around 27% in South Georgia and the Black Belt. The caption for this illustration, then, might well read "What a Difference Four Years Can Make!" This is true especially when that span marks the explosive emergence of the sure enough, in your face, in-the-street and in-full-view of the cameras "protest" phase of the civil rights movement. The stubborn and sometimes openly violent resistance that met the Freedom Riders, the Sit-Inners, and other demonstrations against economic and social discrimination and denial of the right to vote finally forced an extremely reluctant John F. Kennedy to stop simply talking about civil rights and finally do something. Sending troops to Ole Miss and Birmingham and dispatching brother Bobby to sprint to the head of the March on Washington in 1963, pretty much did "the Kennedys" in with a great many white Southerners, and the actions in 1964 of the traitorous Texan, Lyndon B. Johnson, in pushing through the most far-reaching piece of civil rights legislation in American history would assure that his observation that the Democrats had likely lost the South "for a generation" quickly earned a prominent place in the Understatement Hall of Fame.
This became clear enough in the 1964 presidential campaign in which Republican Barry Goldwater vowed to "go hunting where the ducks are" by using his vote against the Civil Rights Act of 1964 to persuade white Southerners to abandon the party of their hallowed forefathers. Goldwater disdained any effort in the South even to retain the support of a vestigial core of middle-class black Republicans that dated all the way back to Reconstruction. Hence his 87 percent tally in Mississippi amounted to what was virtually an all-white landslide in that state. Although white voters in Georgia manifested more resistance to his charms, the dramatic about-face in voting was shocking even to seasoned political observers. Where his Republican predecessor claimed 37% of the Georgia vote in 1960-- including the majority of black votes in Atlanta, Goldwater, with hardly a black supporter to his name grabbed 54 percent of the ballots cast. In South Georgia and the Black Belt, the curmudgeonly Arizonan captured better than 60 percent of the vote, more than doubling Nixon's numbers. In many individual counties, Goldwater's share of the vote approached and in some cases even exceeded Kennedy's from four years earlier. In Calhoun County, for example, Kennedy had claimed 79 percent of the vote in 1960 but 86 percent went to Goldwater in 1964. The Voting Rights Act would not get on the books until the following year, and thus only 6 percent of the voting age black population of the 60 percent black county could even cast a ballot in 1964. Twenty years later, black voters would see to it that Calhoun County gave a solid majority to Democrat Walter Mondale, a liberal Mr. Rogers to Goldwater's conservative Cookie Monster. If, however, the Democrats hoped to offset their losses from white defections with newly enfranchised black loyalists, they were sorely disappointed, for nearly 3 million more whites than blacks registered to vote in the South over the course of the 1960s, and even with one of their own heading the ticket in 1976, the majority of this greatly expanded white electorate would never cast another Democratic vote in a presidential election.
For a time, to be sure, many of these folks insisted "I never left the Democratic party. It left me." The most telling evidence of Ronald Reagan's impact on southern politics may be that while only 40 percent of southern white conservatives identified themselves as Republicans in 1980, eight years later, that figure stood at 60 percent. Reagan's persuasiveness and charm clearly played a key in selling a less blatantly racialized version of the old Goldwater southern strategy, one that emphasized maximizing and safeguarding the fruits of individual achievement (as measured by economic success) over fostering social responsibility. It also favored neighborhood autonomy (suburban neighborhoods that is) over equality of opportunity or access, all the while casting the central city and the federal government as the principal threats to the freedom of honest, God-fearing whites to enjoy the rewards attendant to their accomplishments. As the twenty-first century began, there were arguments that the old "southern strategy" had now become instead a "suburban strategy" that worked in white neighborhoods surrounding not just Atlanta or Birmingham but any number of northern cities as well. This explanation helped to explain the GOP's appeal to southern white suburbanites, but it failed to account for the continued Republican appeal to whites living beyond the southern metropolis. The raw numbers behind recent Republican majorities in the South may have come from the suburbs, but the intensity of GOP support was arguably greatest among white voters with lower incomes living in rural areas and towns too small to incorporate true neighborhoods.
Across the South in 2004, George W. Bush averaged 55 percent of the vote in metro counties and 60 percent in rural counties; his poorest showings were in urban core or central city counties and rural counties with relatively large black population percentages. Support for Bush along the I-85 corridor between Atlanta and Charlotte fit a national pattern--voters in counties just outside metropolitan areas voted for him at higher percentages than those actually within the areas themselves. His most ardent supporters in this part of the South, however, were whites in rural counties even farther from metro areas, where he collected 63 percent of the vote. Of the eight Georgia counties that gave John McCain at least 80 percent of their votes in 2008, five were 100 percent rural; one was 99 percent and another 94 percent. A Republican strategist may have been correct in assuming in 2004 that "if you drive a Lincoln or a BMW and you own a gun, you're voting for George Bush," but the most loyal and dependable support that Bush enjoyed in the South came from voters well acquainted with guns but more likely to be struggling to make the payments on a Ford or Chevrolet pickup than cruising contentedly around in a Lincoln or Bee-mer. In 2008, the correlation between white household income and support for McCain in Georgia counties was actually slightly negative. On the other hand, the percentage of all households that were white was far and away the best single predictor of a county's GOP proclivities. This combo map (Dark Green=Whiter,more Repub,) courtesy of the wonderful folks at the Georgia Statistics System--check'em out, you'll see what I mean--is a window not just on the politics of Georgia, or even the South, but on the nation.
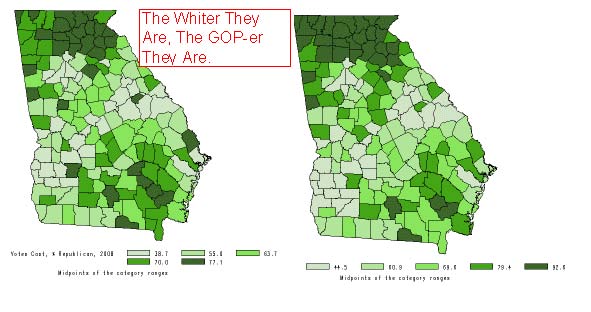
Purely and simply, here in Georgia and damn near everywhere else in this great nation of ours, the most Republican places are most likely anywhere that's overwhelmingly rural and white. The Repubs may be preaching to the 'burbs nowadays, but, even if the text has been upgraded, the folks out in the boondocks know the real message hasn't changed.